Repmold represents a breakthrough in advanced mold-making. The term itself comes from “replica” and “mold,” reflecting its role in creating exact duplicates of designs with precision at scale.
Traditional mold-making relied on time-consuming manual work, but repmold changes the rules by combining digital manufacturing and industrial automation to deliver reliable results much faster.
At its essence, repmold is about replication at scale. Instead of weeks or months, molds can be created in days. This means industries achieve shorter product cycles, bringing new products to market faster and at lower cost.
Engineers see repmold as a strategic manufacturing tool, one that ensures consistency, reduces waste, and supports sustainability goals in production. It goes beyond just making molds—it’s about reshaping how industries work and compete in a fast-changing global economy. Let’s dive in!
From Traditional to Modern: The Evolution of Mold-Making
Mold-making has been around for centuries. In early civilizations, artisans carved molds from stone, clay, or wood. Each piece required hours of effort, and results varied depending on skill.
With the industrial revolution, factories embraced steel and iron molds, allowing industrial tooling to drive mass production. This shift fueled global trade shifts and gave rise to new manufacturing systems.
Even as factories expanded, older techniques remained slow. Injection molding improved efficiency but still required long lead times to prepare the first mold. Companies wanted to achieve shorter product cycles and more design iterations without compromising quality.
Repmold emerged as the solution, bringing together computer-aided design (CAD), CNC machining, and additive manufacturing. It signaled a move away from labor-intensive processes toward industrial innovation, where speed and accuracy exist side by side.
Core Principles and Technical Framework
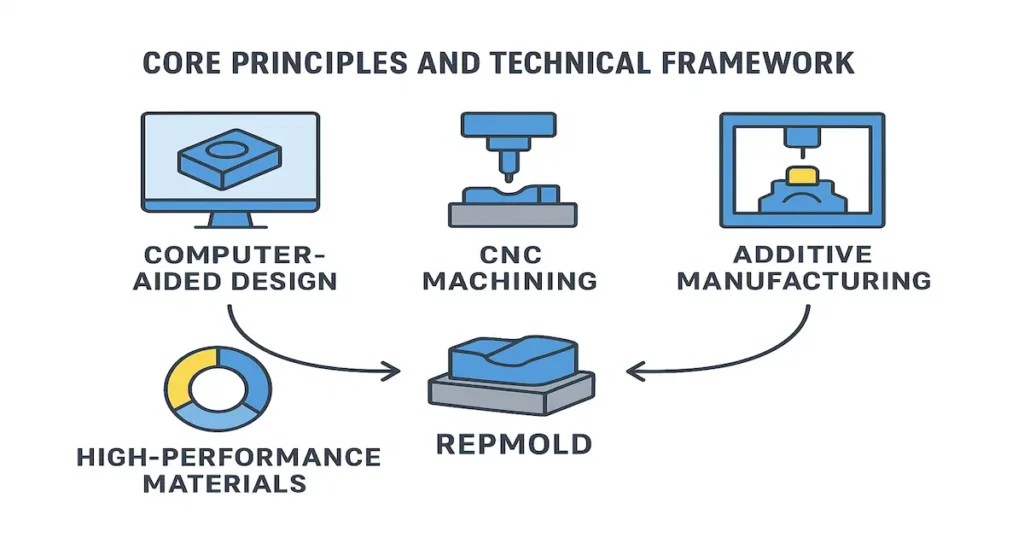
Repmold works through a digital-first process. It begins with computer-aided design (CAD), where engineers create and test a part virtually. This digital model is refined until every detail is correct.
Once ready, the design is translated into physical form using CNC machining or additive manufacturing. This approach to prototyping technology eliminates guesswork and reduces costly mistakes.
Read More: The Smart Choice for Quality Glassware: W J Redmond Dose Glass
The materials used also matter. High-performance polymers, alloys and composites, and eco-friendly materials give molds durability and adaptability. Combined with automation in mold-making, these materials improve strength and extend mold life.
A production expert explained it clearly: “Speed used to be the enemy of quality. Repmold proves they can coexist.” The integration of tools, processes, and materials makes repmold a complete system, not just a single step in manufacturing.
Industrial and Practical Applications
Repmold finds use across multiple sectors. In the automotive industry, it supports rapid prototyping of dashboards, engines, and frames, allowing teams to perform fast design iterations before mass production begins.
Aerospace engineers rely on repmold to create precise, lightweight parts that meet strict safety rules.
Medical applications are also expanding. Surgeons and researchers use customized molds for individualized products such as implants, prosthetics, and device casings.
In electronics, repmold supports time-to-market goals by allowing new smartphones and wearables to reach customers faster.
Even in construction, repmold is shaping the future by creating modular components for buildings, making large-scale projects faster, safer, and more efficient.
Advantages of Repmold Over Conventional Methods
Repmold delivers a clear set of advantages over traditional methods. The most obvious is speed.
Rapid prototyping reduces waiting time, while shorter product cycles help industries respond to demand quickly. This leads to a direct cost reduction in manufacturing, since less time, energy, and raw material are wasted.
Consistency is another strength. Every mold produced with repmold maintains high quality and accuracy. By using eco-friendly resources for molds, repmold also supports sustainable manufacturing.
These factors make it a game-changer for industries that depend on safety, precision, and scalability.
| Aspect | Traditional Mold-Making | Repmold Technology |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Weeks to months | Days to weeks |
| Cost | High investment | Lower digital costs |
| Flexibility | Limited materials | Polymers, alloys, composites |
| Accuracy | Manual skill needed | Automated with CAD and CNC |
| Scalability | Moderate | High and efficient |
Limitations and Challenges in Adoption
While repmold has many advantages, it also faces challenges. Initial setup is costly. Companies must invest in CNC machining, design software, and skilled labor. Though cheaper than traditional mold-making in the long run, these early costs can slow adoption.
Workforce readiness is another obstacle. Many employees need to meet training requirements for digital skills to operate repmold systems. There are also intellectual property risks, since rapid copying may encourage unauthorized duplication.
Additionally, some materials made with alloys and composites may not match the durability of forged molds. Overcoming these issues requires investment, planning, and careful management.
Economic, Social, and Cultural Impacts
The economic value of repmold is clear. By enabling smaller firms to adopt advanced methods, it reduces barriers to entry and encourages competition.
It supports job creation in advanced manufacturing and strengthens global competitiveness. Lower costs and faster delivery also benefit customers by making products more accessible.
Culturally, repmold represents a shift in values. It reflects digital precision vs artisanal craftsmanship, where technology enhances creativity instead of replacing it.
Also Visit: Xuebaotou: The Iconic Face of Academic Pressure and Digital Identity
For many industries, repmold is more than a process—it’s a strategic manufacturing tool that defines progress. It balances heritage with industrial innovation, aligning with modern sustainability goals in production.
| Impact Area | Positive Effect of Repmold |
|---|---|
| Economy | Lower barriers, higher competition |
| Jobs | More opportunities in design, quality, and production |
| Culture | Blend of tradition with digital innovation |
| Sustainability | Reduced waste, eco-friendly materials |
| Industry Growth | Better flexibility and efficiency |
Future Directions and Innovations
The future of repmold is closely tied to AI integration in manufacturing. Artificial intelligence will help design smarter molds, predict wear, and reduce downtime. By using sensors and data analysis, repmold systems will deliver even greater manufacturing efficiency.
Another path lies in biomanufacturing. Here, repmold may create molds that replicate living tissues for medical research. Growth in custom fabrication will also rise, allowing industries to produce customized molds for individualized products on demand.
The use of eco-friendly resources for molds will expand, driving sustainability goals in production and supporting future lean production models.
| Future Trend | Impact on Repmold |
|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence | Smarter, self-learning designs |
| Biomaterials | Expansion into health and medicine |
| Customization | Greater personalization in products |
| Green Resources | Eco-friendly molds and sustainability |
| Industry 4.0 | Fully connected smart factories |
Conclusion and Key Takeaways
Repmold is the natural evolution of advanced mold-making. It combines automation in mold-making, new materials, and digital tools to deliver both replication at scale and precision at scale.
Its influence spreads across automotive, aerospace, medicine, construction, and electronics, redefining how industries work.
The benefits—speed, cost savings, flexibility, and sustainability—far outweigh the challenges. It is both a reminder of progress and a strategic manufacturing tool shaping the future.
While there are hurdles such as high startup costs, intellectual property risks, and training requirements for digital skills, the long-term promise of repmold is undeniable.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is repmold and how does it work?
Repmold is a method of creating precision molds using CAD, CNC machining, and additive manufacturing. It allows replication at scale with faster results and lower costs compared to traditional methods.
How does repmold differ from traditional mold-making?
Traditional methods depend on manual craftsmanship and take longer to produce molds. Repmold uses digital manufacturing and automation in mold-making, giving industries the ability to achieve shorter product cycles and more consistent results.
What industries benefit most from repmold?
Industries such as automotive, aerospace, healthcare, consumer electronics, and construction gain the most. Each uses repmold for rapid prototyping, design iterations, and custom fabrication of parts.
What challenges does repmold face?
Challenges include high upfront costs, training requirements for digital skills, material limitations, and intellectual property risks. These challenges can be addressed with investment in technology and workforce development.
What is the future of repmold?
The future includes AI integration in manufacturing, growth in biomanufacturing, wider use of eco-friendly resources for molds, and expansion into personalized products. These shifts align with sustainability goals in production and ensure greater global competitiveness.












