In today’s digital age, we generate and store massive amounts of data every day. From personal files like photos and videos to business documents, understanding how data is measured and converted between units like gigabytes (GB), terabytes (TB), and even petabytes (PB) is essential for effective storage management.
This knowledge not only helps you make informed decisions about how much storage you need but also saves time, money, and ensures that your data is accessible when you need it.
In this article, we’ll break down key concepts around data conversion, explain how different storage units work, and provide practical tips to optimize your storage solutions.
Lets get started!
What Does “14901.98 to TB” Mean?
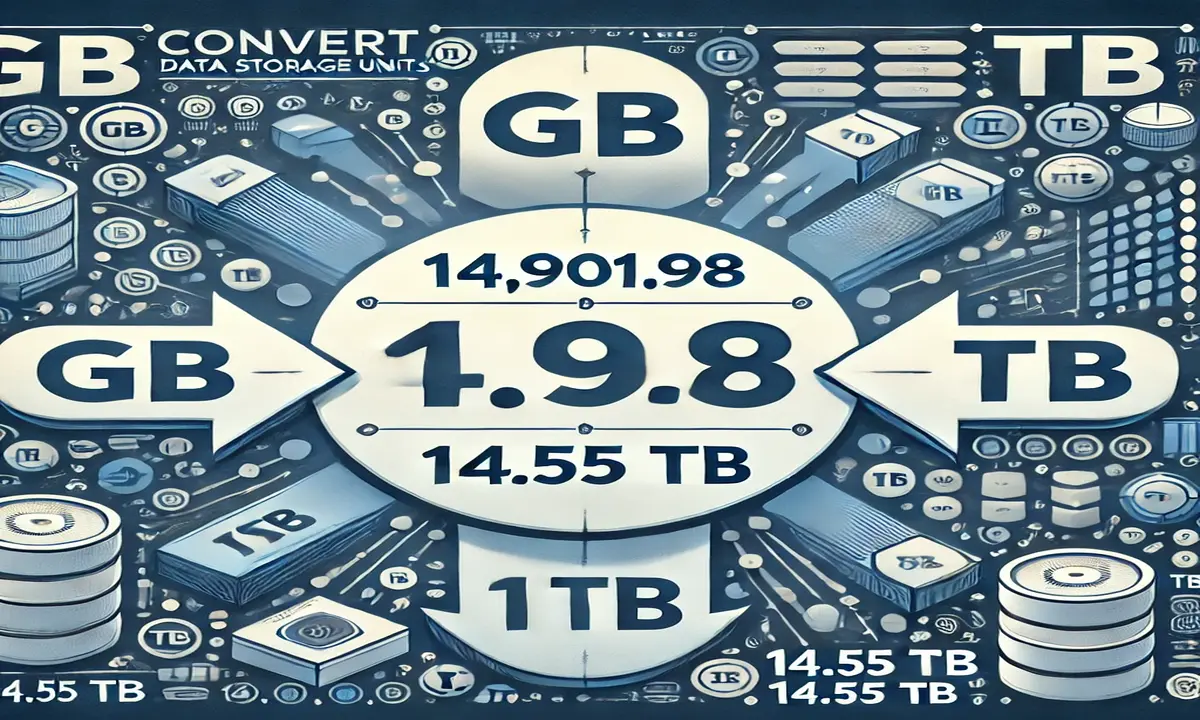
When discussing data storage, understanding the units of measurement is crucial. “14,901.98 to TB” refers to converting a storage quantity, which is slightly more than 14,901 gigabytes (GB), into terabytes (TB).
Terabytes (TB) represent a larger unit used to measure digital information, commonly used in enterprise systems, gaming, video editing, and cloud storage solutions.
To grasp what “14,901.98 to TB” means, it’s important to first understand how terabytes fit into the broader data measurement system. Data is typically measured in bytes, kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB), terabytes (TB), and even larger units for advanced data needs.
This hierarchy helps manage data efficiently, ensuring files are appropriately sized for the devices they are stored on or shared across. Otherwise, using the wrong file sizes can cause delays, system overloads, or even data loss.
Understanding Data Units
Before we delve into the nuances of conversion, it’s important to grasp the basic storage units:
- Byte (B): The smallest unit of data. A single character (like a letter or number) typically takes up one byte.
- Kilobyte (KB): 1,024 bytes. This is a small unit often used for simple files like text documents or small images.
- Megabyte (MB): 1,024 kilobytes. This unit is commonly used for slightly larger digital files, like pictures or short audio clips.
- Gigabyte (GB): 1,024 megabytes. A common unit for storage space, used for apps, large images, or video clips.
- Terabyte (TB): 1,024 gigabytes. This unit is often used for more extensive storage needs, such as large video editing projects, databases, or backups.
- Petabyte (PB): 1,024 terabytes. A massive unit, used for handling large-scale datasets like those used in cloud computing or data centers.
- Exabyte (EB): 1,024 petabytes. Used in industries where extremely large-scale data processing and storage are necessary, such as scientific research.
The Difference Between GB and TB
The gigabyte (GB) and terabyte (TB) are two of the most commonly used units, but they serve vastly different purposes:
- Gigabyte (GB): This is often used for more common storage needs, like saving photos, documents, and audio files. One gigabyte can hold thousands of songs or dozens of HD movies.
- Terabyte (TB): A much larger unit, terabytes are used for bulk data storage—like video editing projects, long-term data backups, or large business databases. One terabyte can store hundreds of thousands of photos, several hours of HD video, or tens of thousands of documents.
Why Converting GB to TB is Important
Understanding the conversion between GB and TB helps with planning your storage needs and ensures you don’t run out of space too quickly.
One terabyte equals 1,024 gigabytes (GB), which can feel overwhelming at first, but once you grasp it, it becomes easy to manage your data more efficiently.
For example:
14,901.98 GB ÷ 1,024 = 14.55 TB.
So, if you have 14,901.98 GB of data, that equals approximately 14.55 terabytes. This kind of conversion is particularly useful for businesses or individuals managing large video projects or extensive datasets.
Also Read: Error Code FintechAsia
Practical Applications of Data Conversion
Understanding data conversions isn’t just about theoretical knowledge—it has real-world applications across various areas:
- Personal Media: Photos, videos, and music files are common forms of data we deal with every day.
Knowing how much space different media types require helps you manage your storage efficiently. For example, a high-resolution image might take 5 MB, and if you have 10,000 photos, you’ll need around 50 GB for all those images. - Video Editing: Videos consume a significant amount of storage. A one-hour HD video can range from 3 to 5 GB, depending on the quality. If you’re editing several videos each week, you’ll need to account for this data usage and plan your storage accordingly.
- Business Data: For companies, data conversion is crucial when managing extensive customer records, marketing analytics, or financial data. Business datasets can quickly grow into multiple terabytes, so knowing how much data you’re working with ensures efficient backup solutions and scaling decisions.
Why Conversion Matters in Storage Management
Converting between storage units doesn’t just help you calculate space; it plays a critical role in making better decisions about data management, cost-efficiency, and system performance:
- Cost Efficiency: Knowing the data size can help you make smarter storage decisions. For example, if you know your data will grow to multiple terabytes over time, investing in scalable cloud storage might save you money compared to purchasing physical hard drives.
- Optimizing Performance: Some storage solutions are better suited for performance, while others are optimized for large volumes of data. For instance, SSDs (Solid State Drives) are faster than HDDs (Hard Disk Drives) but come at a higher cost.
Knowing your data size helps you choose the right type of storage based on speed vs. cost. - Scalability: Data grows—both in volume and complexity. Understanding conversion helps you plan for the long term. Whether you’re expanding your business data storage or backing up personal files, converting between units allows for more strategic planning.
Examples of How Different Storage Units Work
Let’s break down a few real-world examples to see how storage units interact:
- One Hour of HD Video: A high-definition video can take 3 to 5 GB per hour. If you’re storing a significant amount of video content, you’ll need to calculate accordingly—like how much storage a weekend’s worth of video might consume.
- 10,000 High-Resolution Photos: A single photo can be 5 MB in size. If you have 10,000 photos, that totals around 50 GB of storage.
- A Single Day of Business Data: Large businesses that handle datasets like customer interactions, sales analytics, or marketing reports can quickly accumulate terabytes of data, requiring careful storage management.
How to Convert 14901.98 to TB Using Simple Steps
Converting GB to TB is relatively straightforward once you understand the conversion factor:
1 Terabyte (TB) = 1,024 Gigabytes (GB)
To convert GB to TB:
- Divide the number of GB by 1,024.
- For example, if you have 14,901.98 GB:
This formula helps you estimate how much space your files will occupy in larger storage units.
Common Mistakes in Data Conversion
While data conversion is simple, mistakes can happen, especially when rounding off too soon or not using accurate tools. Some common errors include:
- Overlooking Binary Prefixes: It’s easy to confuse binary prefixes like KB, MB, GB, TB (which are based on powers of 2) with decimal units (KB, MB, GB, TB in decimal terms are based on powers of 10). Always use binary conversion unless you specifically need decimal.
- Incorrect Assumptions: Thinking that 1 GB = 1,000 MB is a common pitfall—remember, 1 GB = 1,024 MB.
- Ignoring Precision: Small differences in conversion can add up, especially when dealing with large datasets. Always use precise calculators or tools to avoid cumulative rounding errors.
Optimizing Storage Based on Conversion Insights
Once you understand data conversion, you can implement strategies to make your storage more efficient:
- Compression: Compressing files reduces the space they take up without sacrificing quality. Tools like ZIP or modern compression algorithms can significantly lower file sizes.
- Cloud Storage: Cloud storage solutions allow you to scale up or down depending on your needs—use cloud storage wisely to expand storage as you grow.
- Backup Strategies: Knowing how much data you’ll store allows you to create smarter backup solutions—whether you’re using external drives or cloud-based backups.
The Future of Data Storage
As data continues to grow exponentially, storage solutions are becoming more advanced:
- Cloud-Based Storage: Cloud storage allows businesses and individuals to access vast amounts of storage on-demand, without the need to maintain physical servers or drives.
- Edge Computing: This technology brings computing power closer to where data is generated, enabling faster processing of data at the point of origin—reducing the need to send large datasets across networks.
- AI-Powered Data Management: AI is starting to play a huge role in analyzing data patterns and predicting storage needs, helping businesses manage storage in more intelligent ways.
Conclusion
Understanding data conversion—from gigabytes to terabytes—is essential for making efficient storage decisions.
Whether you’re a personal user, a small business owner, or managing large datasets at a corporate level, knowing how to convert between these units helps you plan for data storage, scaling, and performance.
By following the steps outlined here and avoiding common mistakes, you’ll be better equipped to handle your storage needs effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between GB and TB?
GB (Gigabyte) is smaller than TB (Terabyte). 1 TB equals 1,024 GB.
Why is converting data to TB important?
Converting data to TB helps you estimate storage space needed for larger files, like videos or extensive data sets, and plan your storage efficiently.
How can I avoid mistakes in data conversion?
Always use precise tools, avoid rounding off too soon, and be aware of binary prefixes. Double-check calculations and use reliable converters.
What is a petabyte (PB), and how does it relate to TB?
A petabyte (PB) equals 1,024 terabytes and is used for massive data storage in data centers, cloud computing, or scientific research.
What’s the easiest way to calculate how much storage I need?
Start by identifying the size of the files you’re storing (like photos, videos, documents), then use conversion to estimate how much space you’ll need.